
| OBDII : B-Codes C-Codes U-Codes P-Codes |
DiagnosticTrouble.com was developed by experts in automotive service industry to help diagnose cars and assist in troubleshooting procedures.
Diagnostics Trouble Codes (DTCs) are codes that the vehicle's electronic control unit generates when it detects malfunction or other issues.
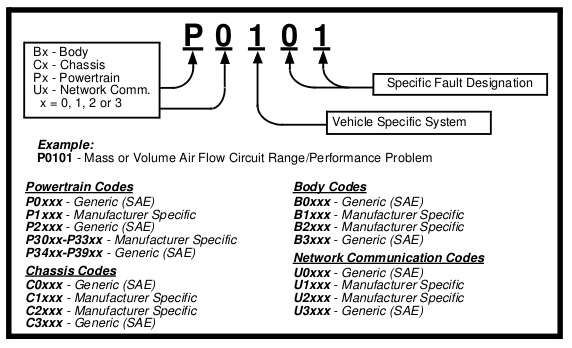
The codes in all these different types are grouped into four categories:
The OBD 2 Diagnostics trouble process is preformed by your cars onboard computer system using sensors located throughout your car's engine, drive train(p), chassis(c), body(b), and network communication(u) systems. Some fault codes indicate real problems with your vehicle and some indicate faulty sensors
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) are meant to guide you to the proper service procedure in the vehicle's service manual. DO NOT replace parts based only on DTCs without first consulting the vehicle's service manual for proper testing procedures for that particular system, circuit or component. DTCs are alphanumeric codes that are used to identify a problem that is present in any of the systems that are monitored by the on-board computer (PCM). Each trouble code has an assigned message that identifies the circuit, component or system area where the problem was found.
DTCs are alphanumeric codes that are used to identify a problem that is present in any of the systems that are monitored by the on-board computer (PCM). Each trouble code has an assigned message that identifies the circuit, component or system area where the problem was found. OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes are made up of five characters:
When the vehicle's on-board computer detects a failure in an emissions-related component or system, the computer's internal diagnostic program assigns a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that points to the system (and subsystem) where the fault was found. The diagnostic program saves the code in the computer's memory. It records a 'Freeze Frame' of conditions present when the fault was found, and lights the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). Some faults require detection for two trips in a row before the MIL is turned on.
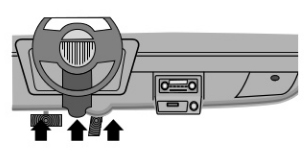
Data link connector location is under dashboard on driver side of car.
If data link connector is not located under dashboard, a labe should be there telling where the connector can be found.
| Powertrain Codes | Network Codes | Chassis Codes | Body Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
To extract and read DTC fault codes, you need a diagnostic connector and a DTC scanner. The DTC code reader or scanner shows codes in one-line descriptions or includes code definitions.
Diagnostic connectors aren't universal, so if your vehicle diagnostic connector were manufactured before 1996, it'd need specific adapters.
Newer car models typically have the same connectors
Here's how to extract DTC codes from your car:
Sometimes when a Check Engine Light comes on the vehicle's engine computer will go into a "back-up" or "limp-home" mode. This allows the vehicle to continue operating until repairs can be made. Back-up or limp-home modes are not the most emission or fuel efficient way for the vehicle to operate. The problem needs to be repaired.
The Check Engine Light will stay on until the readiness monitor related to that fault has been reset and the sensor that was recorded out-of-range is seen as within range again.